The Historical Journey of Horticulture
The origins of horticulture can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early humans began to domesticate plants and cultivate them for food, medicinal purposes, and ornamental use. This pivotal shift in lifestyle, from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled agricultural societies, marked the dawn of horticulture as a structured practice. In regions such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, horticultural methods were critical to the development of stable food sources, facilitating population growth and urbanization.

As these early societies progressed, horticultural practices played a significant role in ensuring food security. The cultivation of fruit and vegetable crops became essential to sustaining communities, leading to the establishment of local markets. The ancient Greeks and Romans further advanced horticulture by introducing systematic planting techniques and diverse crop rotations, which laid the groundwork for future agriculture. The Greeks valued gardens not only for food production but also for their aesthetic and therapeutic qualities, showcasing the multifaceted nature of horticultural endeavors.

The transition from subsistence gardening to commercial horticulture occurred during the Middle Ages, as advancements in trade and exploration expanded agricultural boundaries. The dissemination of knowledge, along with the introduction of new plant species from various regions, enriched horticultural practices. Key milestones such as the establishment of botanical gardens in Europe emphasized the importance of horticulture in education and research. The Renaissance period witnessed influential figures, including botanists and plant breeders, who contributed to the evolution of horticulture as a scientific discipline.
Technological advancements in the 19th and 20th centuries, including the development of greenhouses, irrigation systems, and modern cultivation techniques, further transformed the field. The rise of commercial horticulture marked a significant turning point, whereby horticultural practices began to meet the demands of an increasingly urbanized population. This evolution reflects not only the history of horticulture but also its vital role in shaping societies and economies throughout time.
-
Ancient Civilizations → Pyramids / early farming scene
-
Classical Era → Greek or Roman garden / vineyard
-
Medieval Period → Monastery garden / Islamic garden
-
Renaissance → Old botanical garden / books on plants
-
17th–18th Century → Globe / explorers with crops
-
19th Century → Ornamental flower gardens / horticultural society meeting
-
20th Century → Greenhouse with crops
-
21st Century → Vertical farming / drone in agriculture
Branches of Horticulture: An Overview
Horticulture is a diverse field encompassing various branches that contribute significantly to food production, environmental sustainability, and aesthetic values. The major branches of horticulture include pomology, olericulture, floriculture, and landscape horticulture, each playing a vital role in the broader horticultural landscape.
Pomology is dedicated to the cultivation and study of fruit-bearing plants. This branch focuses on the improvement of fruit varieties through breeding techniques and the establishment of sustainable cultivation practices. It plays a crucial role in enhancing food security and nutrition by increasing the availability of diverse fruits. Examples of pomology include apple, pear, and citrus cultivation, which are essential in both local and global markets.
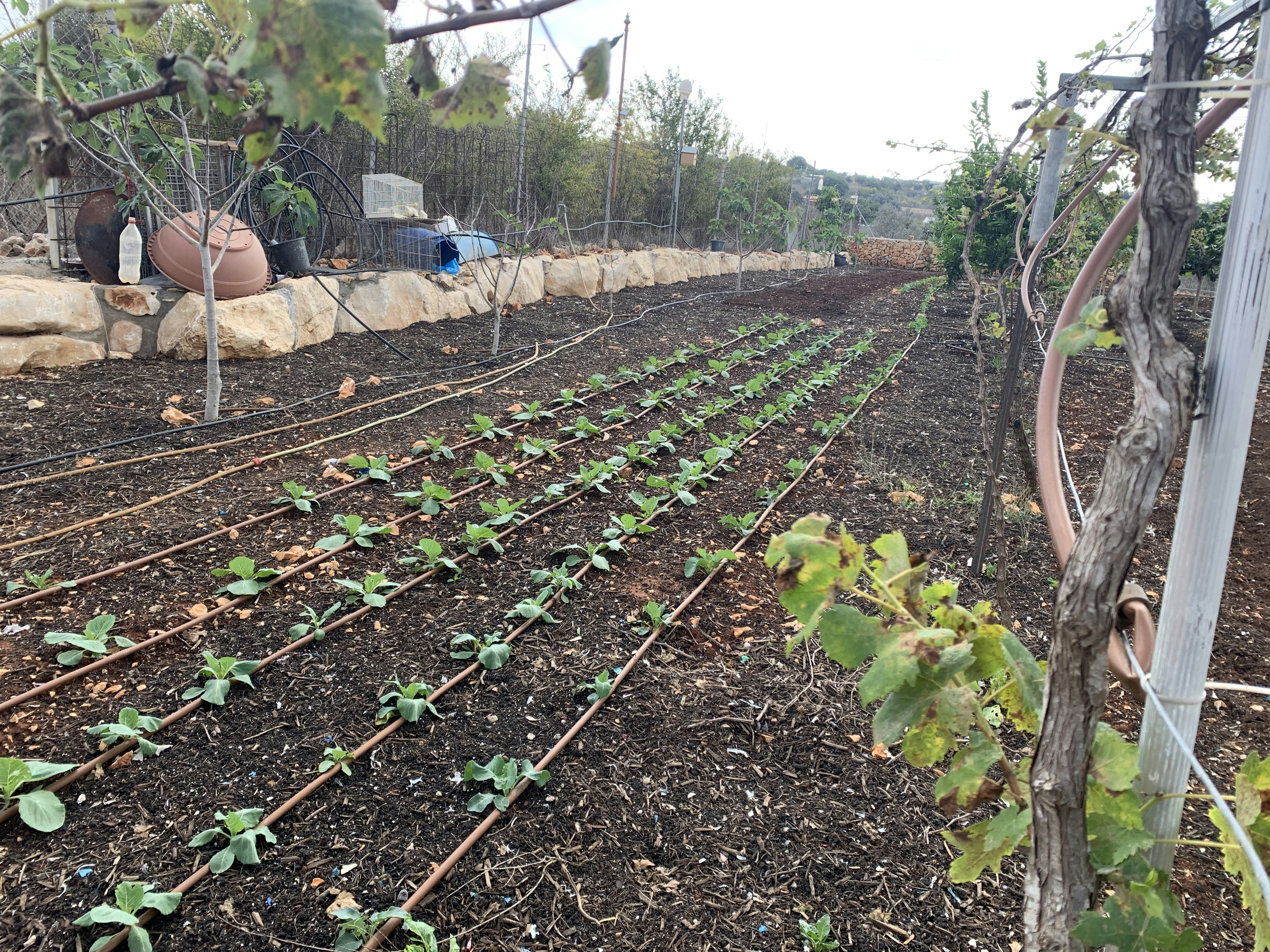
Olericulture, on the other hand, centers on vegetable production. It encompasses the cultivation, harvest, storage, and marketing of vegetables, integral to human diets. Olericulture contributes to nutrition and health by promoting a variety of vegetables, such as tomatoes, carrots, and leafy greens, which are essential for balanced diets. Advances in this branch, including organic farming practices and hydroponics, have made it possible to produce vegetables in urban settings as well.
Floriculture is focused on the cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants, contributing to both the aesthetic enhancement of landscapes and the floral industry. This branch includes the production of cut flowers, potted plants, and landscaping designs, making it significant for residential, commercial, and public spaces. The importance of floriculture is evident during occasions such as weddings and holidays, where flowers serve both symbolic and decorative purposes.
Lastly, landscape horticulture combines elements of design and cultivation to create functional and aesthetically pleasing outdoor areas. This branch involves the planning and maintenance of gardens, parks, and green spaces, contributing to environmental sustainability and improved quality of life. The interconnection between these branches of horticulture highlights their collective impact on biodiversity and sustainable practices, underscoring the importance of horticulture in our daily lives.

Modern Applications of Horticulture in Business
The contemporary landscape of horticulture demonstrates its significant integration across various business sectors, reflecting a dynamic response to the ever-evolving demands of the market. Horticultural practices are now an indispensable component of agribusiness, as they enhance productivity and sustainability. By employing advanced techniques like precision agriculture and hydroponics, businesses optimize resource use while meeting the growing consumer preference for high-quality, organic produce.
Retail has also witnessed a transformation through horticulture. Grocery stores and specialized markets increasingly prioritize locally sourced products, responding to a surge in consumer demand for fresh and organic options. This shift not only fosters community connections but also supports local economies by reducing supply chain distances. In addition, urban farming has gained momentum, providing a novel approach to sourcing food within cityscapes. These practices bridge the gap between urban consumers and agricultural producers, transforming unused vertical spaces into thriving gardens.
Landscaping services exemplify another sector where horticultural methods have been innovatively applied. Landscape architects and designers incorporate sustainable practices that emphasize biodiversity, soil health, and native species selection in their projects. These approaches not only enhance aesthetic values but also contribute to environmental stewardship, making landscapes more resilient and capable of supporting local ecosystems.
To illustrate the practical applications and benefits of horticulture in business, various case studies showcase successful ventures. For instance, companies adopting agritech solutions have reported significant increases in yield and profit margins, driven by consumer trends favoring organic products. These examples highlight the economic impact of horticulture, demonstrating its role in shaping market trends, boosting local employment, and fostering sustainable practices within communities. As the horticulture industry continues to adapt, its contributions are likely to expand, reinforcing its importance in contemporary business landscapes.
The Future of Horticulture: Innovations and Sustainability
The future of horticulture is being defined by a convergence of cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices that promise to reshape how we approach food production and environmental stewardship. As global populations continue to rise, innovative solutions such as hydroponics and vertical farming are emerging as viable alternatives to traditional agricultural methods. Hydroponics, for example, allows for the cultivation of plants in nutrient-rich water rather than soil, significantly reducing the land footprint needed for farming. This method not only conserves water but also enables year-round production, which is crucial for meeting growing food demands.
Vertical farming takes this concept a step further by optimizing space within urban settings. Utilizing stacked layers of crops, these systems can be integrated into city landscapes, thus minimizing transportation emissions while maximizing yield per square foot. This innovative trend not only enhances food security but also contributes to local economies and urban sustainability initiatives. The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, into horticultural practices is also transforming the industry. These technologies allow for precise monitoring and automated systems that optimize plant growth conditions, leading to increased efficiency and reduced waste.
Furthermore, genetic engineering is gaining traction in horticulture, allowing for the development of crops that are more resilient to pests, diseases, and climate fluctuations. This scientific advancement is crucial for adapting to the challenges posed by climate change, ultimately leading to more sustainable food systems. The need for skilled professionals in this rapidly evolving field cannot be overstated. Education and research will play vital roles in equipping the workforce with the necessary skills to leverage these advancements effectively. By prioritizing research initiatives and educational programs, the horticulture industry can prepare for the challenges and opportunities of a sustainable future.





The Silent Language Of Plants: Signal Transduction Pathways
[…] The Evolution and Impact of Horticulture: History, Branches, and Business Applications […]