Introduction to Chromosomes in Genomics
Chromosomes are long strands of DNA that house our genetic material. They play a crucial role in the process of heredity and are fundamental to the study of genomics. In genome-wide analysis, understanding the structure and organization of chromosomes is vital for deciphering genetic information.
The Concept of Scaffolds in Genome Assembly
In the realm of genomics, a scaffold refers to a set of contigs anchored by known landmarks, such as genetic markers. Scaffolds are useful for organizing contigs into a larger framework, which can facilitate the interpretation of genomic sequences. By using scaffolds, researchers can construct a more coherent view of the genome, promoting analysis on a broader scale.
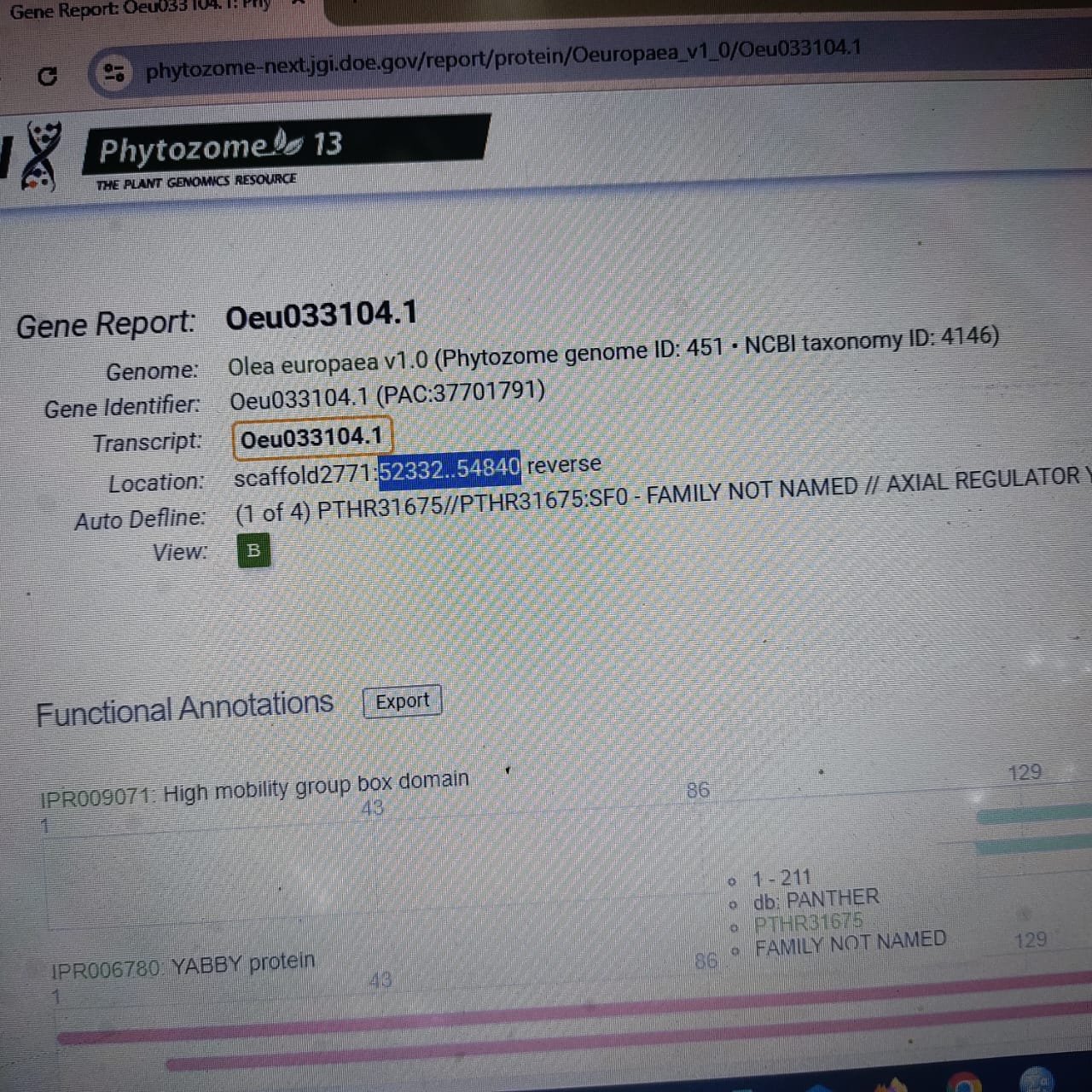
Contigs: The Building Blocks of Genomic Analysis
In summary, chromosomes, scaffolds, and contigs are integral components in genome-wide analysis. By elucidating their roles, researchers can gain valuable insights into the structure, function, and evolution of genomes, paving the way for advances in genetics and molecular biology.

Understanding Source Accession, Chromosome Length, and Protein Length in Genome-Wide Analysis




