Smart Packaging in Horticulture
Smart packaging represents a transformative shift in the post-harvest management of horticultural products. This technology incorporates advanced features such as sensors, RFID tags, and QR codes, facilitating a dynamic interaction between consumers, producers, and products throughout the supply chain. These innovations are pivotal in preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of fresh produce, ensuring that fruits and vegetables maintain their desired freshness during transportation and storage.

The integration of sensors in smart packaging allows for real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and ethylene levels, which are critical factors influencing the quality of perishable goods. By providing this vital information, producers can make informed decisions to optimize storage conditions and reduce waste. Additionally, smart packaging can be equipped with QR codes that enable consumers to access detailed information about the product’s origin, handling, and nutritional content, thereby enhancing transparency and consumer trust.
Moreover, the data collected from smart packaging solutions can offer invaluable insights for supply chain management. Producers and distributors can utilize analytics derived from this data to streamline logistics, improve inventory management, and anticipate demand fluctuations. As a result, businesses can minimize losses attributed to spoilage and ensure that customers receive fresher produce. The relevance of smart packaging in horticulture is further underscored by its potential to support sustainability efforts. By improving the efficiency of supply chains and reducing food waste, smart packaging technologies contribute significantly to environmental preservation.
In essence, the advent of smart packaging in horticulture signifies a major advancement in the way the industry approaches post-harvest management. As innovations continue to evolve, the role of smart packaging will likely become increasingly critical to achieving efficiency, sustainability, and quality assurance in the distribution of fresh horticultural products.


The Integration of IoT in Smart Packaging
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way smart packaging interacts with horticultural products. By embedding sensors in packaging materials, IoT technology enables real-time monitoring of essential environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. This capability is particularly critical in post-harvest horticulture, where the freshness and quality of produce can deteriorate rapidly if not adequately maintained during storage and transportation.
IoT-enabled smart packaging solutions utilize a network of interconnected devices that collect and transmit data. For instance, sensors positioned within packaging can continuously monitor the internal conditions, sending alerts to stakeholders if any parameters deviate from optimal ranges. This proactive approach not only mitigates the risk of spoilage but also enhances the overall efficiency of supply chain operations. The data collected allows producers and distributors to adjust their storage and transportation strategies, ensuring that horticultural products reach consumers in optimal condition.
Several examples of IoT-based smart packaging solutions illustrate the potential of this technology in the horticultural sector. One such innovation involves the use of temperature-sensitive labels that change color if products are exposed to temperatures outside a specified range. This visual indicator serves as a warning signal throughout the supply chain, prompting immediate action to prevent quality loss. Another example is the integration of RFID tags that track product movement, providing real-time visibility into the supply chain and improving inventory management.
As the demand for fresher and more sustainable produce continues to rise, the integration of IoT in smart packaging stands out as a promising solution. By harnessing the power of connectivity and data analytics, stakeholders can make informed decisions that enhance the preservation of horticultural products. The advancements in this technology not only benefit producers and suppliers but also contribute to consumer satisfaction by delivering high-quality fresh produce to the market.
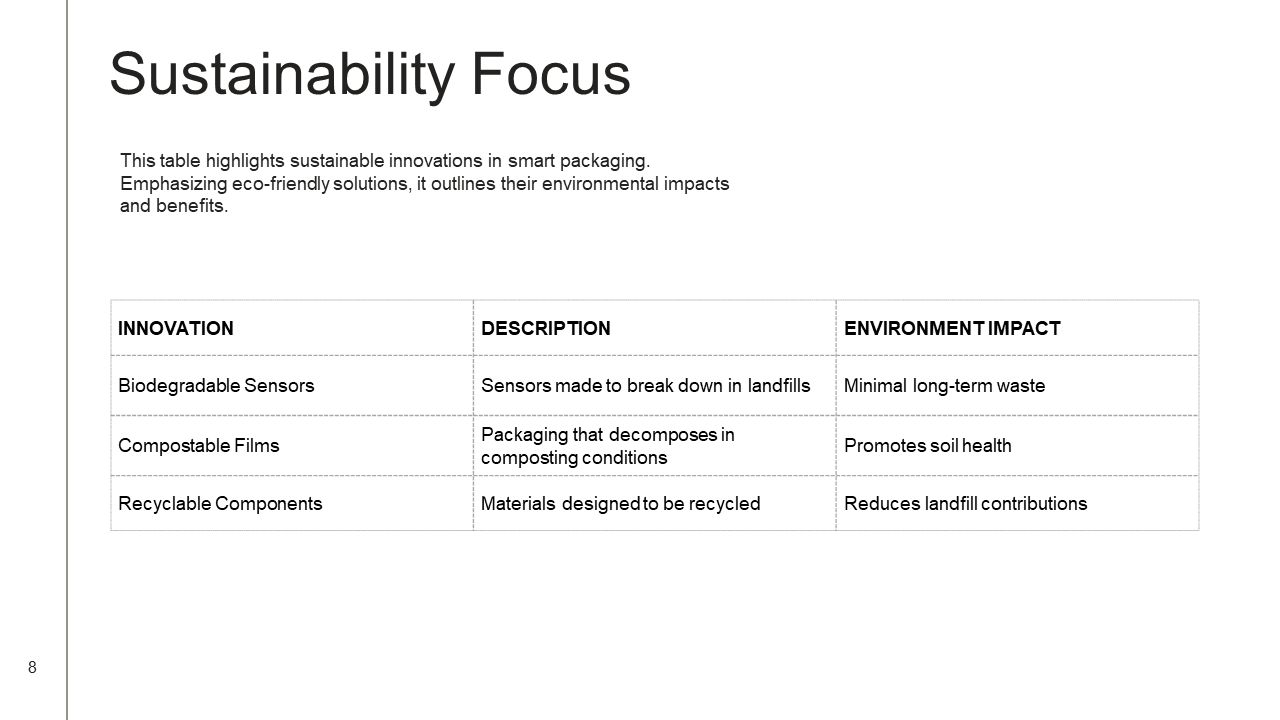
Benefits of Smart Packaging Innovations for Post-Harvest Processes
Smart packaging innovations significantly enhance the post-harvest processes in horticulture, offering a multitude of advantages that benefit producers, retailers, and consumers alike. One crucial benefit is the extension of produce shelf life. By utilizing advanced materials embedded with sensors and smart technology, these packaging solutions can monitor the freshness of fruits and vegetables, proactively responding to environmental changes. This capability not only preserves the quality of the produce but also maintains its nutritional value, ultimately encouraging consumers to purchase and consume fresher products.


Another important advantage of smart packaging is its role in reducing food waste. In the horticultural sector, spoilage often occurs due to inadequate monitoring and management of perishables. With smart packaging, stakeholders can receive real-time data about temperature, humidity, and other critical factors affecting the produce. This allows for timely interventions, minimizing waste throughout the supply chain. Additionally, integrating this technology can significantly enhance traceability. Each smart package can provide detailed information regarding the origin, journey, and treatment of the product, allowing consumers to make informed choices while helping retailers ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Moreover, smart packaging innovations create opportunities for consumer engagement. Interactive features, such as QR codes or augmented reality, can be incorporated into packaging to provide information about the product, including recipes and nutritional benefits. This increased engagement fosters brand loyalty and educates consumers about responsible food choices and sustainability practices.
Economically, these innovations can lead to lower waste management and transportation costs, ultimately supporting a more sustainable supply chain. By streamlining operations and promoting more effective resource use, smart packaging allows the horticultural industry to reconcile its economic objectives with environmental stewardship. The collective benefits of these advancements render smart packaging a transformative element in post-harvest horticulture.




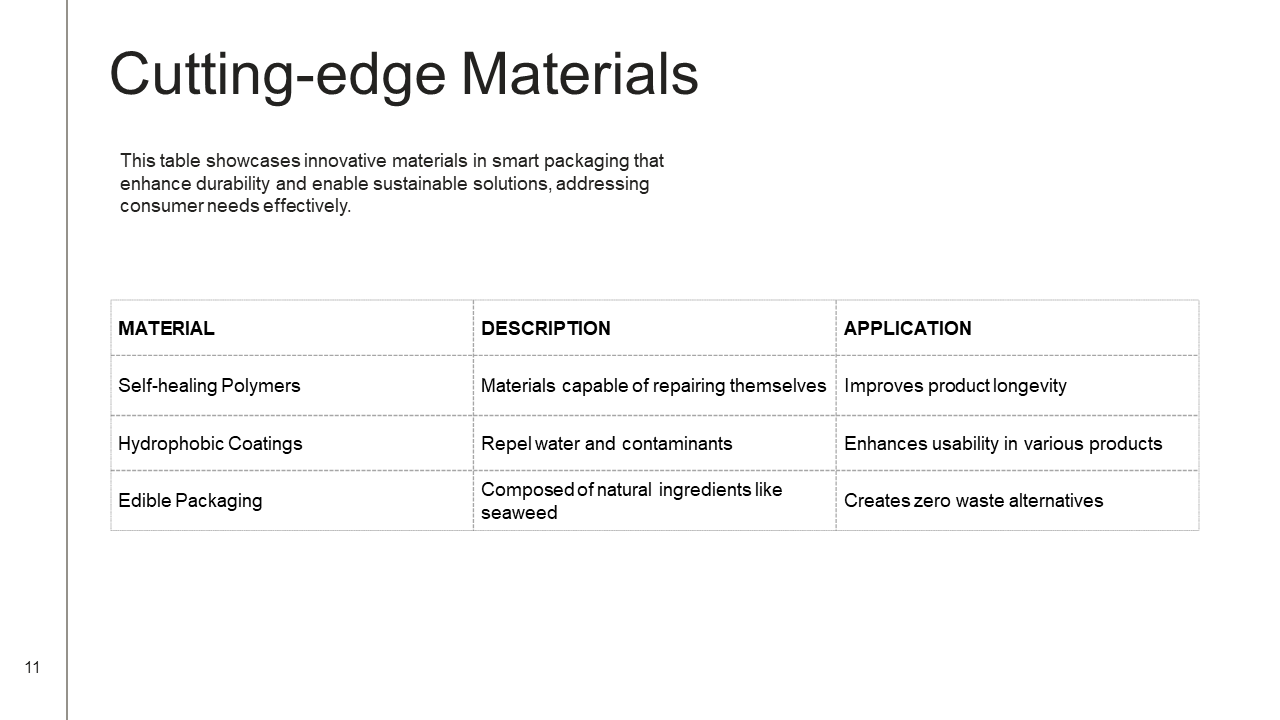
Challenges and Future Directions in Smart Packaging
The adoption of smart packaging innovations within the post-harvest horticulture landscape presents a series of challenges that must be carefully navigated. One of the primary barriers is the cost implications associated with the implementation of advanced technologies. Developing smart packaging solutions often necessitates substantial investment in specialized materials, manufacturing processes, and integration of Internet of Things (IoT) systems. These initial costs can deter small- and medium-sized enterprises from adopting such innovations, potentially widening the gap between larger corporations and smaller players in the market.
Technological barriers also pose significant challenges. The rapidly evolving nature of IoT and smart technologies often leads to a knowledge gap among industry stakeholders. Many growers and distributors may not have the technical expertise required to fully leverage these advancements or maintain the technologies over time. Additionally, the lack of interoperability between different smart packaging systems and devices can hinder seamless communication and data exchange, further limiting overall effectiveness.
Another key challenge is the need for standardization across the horticulture industry. Without established guidelines or protocols, the implementation of smart packaging solutions can be inconsistent, creating difficulties in data comparison and analysis. A lack of standardized metrics can obscure the tangible benefits of smart packaging innovations, making it challenging for stakeholders to assess effectiveness and return on investment.
Looking ahead, however, the future of smart packaging and IoT technology in horticulture remains promising. Anticipated advancements in materials, such as biodegradable and more efficient options, will enhance environmental sustainability. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics is likely to revolutionize decision-making processes, enabling growers to optimize storage conditions and reduce spoilage. Increased interaction with consumers through smart packaging can also provide valuable insights, driving transparency and trust within the supply chain. These emerging trends will shape the next generation of smart packaging innovations, addressing current challenges while fostering growth within the horticultural sector.





Tsum.egomoda.ru
На этом сайте вы сможете найти актуальные промокоды ЦУМ. Применяйте данные купоны, чтобы получить скидки на покупки. Предложения обновляются регулярно, поэтому следите за новыми скидками. Экономьте на товары с выгодными промокодами для ЦУМа.
1win-casino-ng.com
On this website, you will find details about 1Win casino in Nigeria. It covers key features, including the popular online game Aviator. https://1win-casino-ng.com/ You can also discover sports wagering opportunities. Enjoy a seamless gaming experience!
RobertUnsah
На этом сайте вы можете заказать накрутку лайков и фолловеров для социальных сетях , включая ВК, TikTok, Telegram и другие . Оперативная без рисков раскрутка профиля гарантирована . накрутка просмотров на YouTube Выгодные тарифы и надежное выполнение . Начните продвижение уже сейчас !
E-copies.ru
Наш веб-портал — популярное интернет-издание. Мы оперативно размещаем важные новости. https://rftimes.ru/html/smi.html Коллектив журналистов делает всё возможное, чтобы предоставлять достоверную информацию. Следите за нами, чтобы всегда узнавать свежие новости!
FrankFeeda
Max Mara — легендарный известный итальянский бренд, основанный в 1951 году дизайнером Акилле Марамотти. Бренд стал олицетворением безупречного стиля и высокого качества. Фирменный стиль Max Mara сочетает лаконичных форм и премиальных материалов, таких как верблюжья шерсть. Знаменитое пальто Teddy превратилось в одним из самых узнаваемых бренда. http://www.sustainable-everyday-project.net/urbact-socialinnovationincities/?attachment_id=363&unapproved=120989&moderation-hash=3f15d6a868e778343c7e48887494abc2#comment-120989 Сегодня бренд предлагает широкий ассортимент, но и обувь. Max Mara остаётся символом элегантности и класса, завоёвывая модниц по всему миру.
Albertoteede
Jil Sander — это известный немецкий бренд, прославившийся благодаря лаконичному стилю и премиальным материалам. Основанный в 1968 году, он стал символ элегантности. Коллекции марки выделяются чистыми линиями и спокойными оттенками. http://liecebnarieka.sk/forums/topic/blazerifdkf449-4/#post-3162752 Бренд использует натуральными тканями, создавая универсальные вещи для стильного гардероба. Jil Sander ценят за безупречное исполнение и внимание к мелочам. Эти вещи подходят для базового и делового стиля.