Introduction to the Pangenome Concept
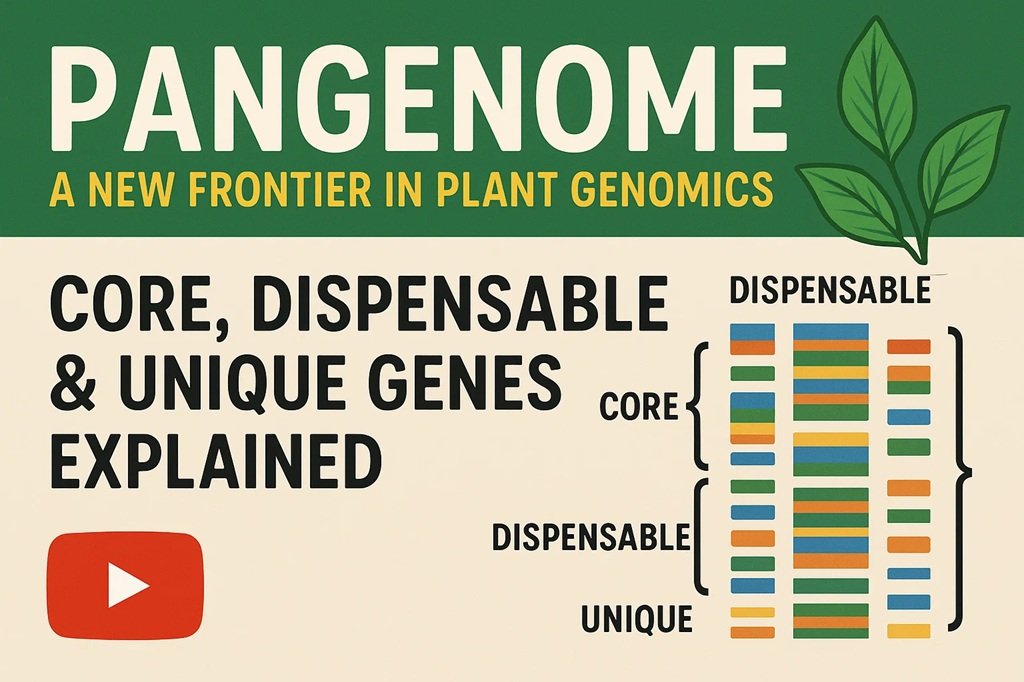
Pangenome is emerging as a pivotal facet in the field of plant genomics. Essentially, a pangenome refers to the complete set of genetic information within a species, encompassing not only the core genome—which consists of genes shared by all individuals within that species—but also the accessory genome, made up of variations that are present in some individuals but absent in others. This comprehensive genetic framework allows researchers to deepen their understanding of the genetic diversity that exists within a species.
In the context of plant genomics, the study of pangenomes has substantial implications for understanding plant biodiversity and adaptation. Each plant species showcases an array of genetic variations that contribute to its resilience and ability to thrive in varying environmental conditions. By exploring the entirety of the genetic variations, scientists can identify specific genes that confer desirable traits, such as drought resistance or enhanced nutritional quality. This not only aids in basic scientific research but also translates into practical applications in agriculture, where breeders can utilize this knowledge to develop improved crop varieties.
The Importance of Pangenomes in Plant Biology
Pangenomes represent a comprehensive genomic framework that encompasses the complete genetic diversity within a species, unlocking new dimensions in plant biology. This expanded view is critical for advancing our understanding of various biological phenomena, such as plant evolution, domestication, and the underlying mechanisms of trait variation. By analyzing the pangenomes of different plant species, researchers can identify genetic variations that contribute to adaptations, thereby shedding light on evolutionary processes that shape plant diversity.
Moreover, pangenomes facilitate the study of domestication, revealing how selective pressures exerted by human activities have influenced the genetic landscape of crops. Through pangenomic analysis, scientists can trace the genetic modifications that have occurred over generations, providing insights into traits that are vital for agriculture, such as yield, drought resistance, and nutritional quality. This sort of understanding can lead to the identification of specific genes that are critical for the enhancement of these traits, thereby paving the way for targeted breeding strategies.
Additionally, the role of pangenomes in crop improvement cannot be understated. With ongoing challenges like climate change and food insecurity, understanding the genetic diversity offered by pangenomes becomes increasingly essential. By harnessing this knowledge, researchers can develop crops that are more resilient to diseases and environmental stresses. The insights gained through pangenome research not only enhance fundamental plant biology but also empower crop scientists to implement effective strategies for enhancing agricultural productivity.
Ultimately, pangenomes serve as a vital tool for unlocking the complexities of plant genetics and evolution. Their significance extends beyond mere academic interest, holding substantial promise for practical applications in agriculture and conservation. As such, the research into pangenomes is not just an exploration of plant biology, but a necessary step towards sustainable agricultural practices that ensure food security for future generations.
Technological Advances in Pangenome Studies
Recent advancements in technology have significantly accelerated the field of pangenome research in plants. One of the most substantial developments has been the emergence of high-throughput sequencing techniques. These innovative methods allow researchers to obtain vast amounts of genomic data in a fraction of the time compared to traditional sequencing methods. The ability to sequence multiple genomes simultaneously enhances the understanding of genetic diversity within plant species, thus providing the foundational data necessary for effective pangenome analysis.
Moreover, the automation and efficiency of high-throughput sequencing technologies have lowered costs, making it more feasible for a greater number of researchers to engage in pangenome studies. The data generated from these sequencing efforts is substantial, requiring advanced bioinformatics tools for comprehensive analysis. These computational tools are essential for assembling and annotating pangenomes, which involves piecing together fragmented genomic information into coherent sequences that represent the full genetic repertoire of a species. The integration of bioinformatics approaches facilitates the identification of gene variations, structural variations, and the functional implications of these differences within and between populations.
The rise of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence has further empowered researchers to handle complex genomic data. These technologies provide predictive models that can unveil patterns not easily discernible by traditional analytical methods. For example, they can aid in predicting plant responses to environmental changes, thereby offering valuable insights into potential adaptations or vulnerabilities of various species under different conditions.
As these technological advances continue to evolve, they hold the promise of unlocking new dimensions in our understanding of plant genomics. The synergy between high-throughput sequencing and sophisticated bioinformatics is setting the stage for groundbreaking discoveries in pangenome studies, ultimately contributing to improved crop resilience and agricultural sustainability.
Case Studies: Pangenome Analyses in Major Crops
Pangenome analyses have emerged as a significant tool in the field of plant genomics, enabling researchers to delve deeper into the genetic architecture of major crops such as rice, wheat, and maize. These studies have provided critical insights into genetic diversity and variation, which are crucial for enhancing crop performance and facilitating breeding strategies.
One of the prominent case studies involves rice (Oryza sativa), where researchers performed a comprehensive pangenome analysis encompassing diverse rice varieties. This study revealed a substantial amount of genetic variation that was previously unexplored. The identification of unique genes and variants not only broadened the understanding of rice’s genetic landscape but also highlighted essential traits related to stress resistance and yield. These findings have direct implications for breeding programs aimed at developing new rice cultivars adapted to changing climatic conditions.
In the case of wheat (Triticum spp.), pangenome research has underscored the evolutionary history of domesticated wheat species and their wild relatives. By analyzing the pangenome, scientists discovered a wealth of alleles associated with disease resistance and grain quality. The insights drawn from this pangenomic framework have informed breeders about the most promising genetic resources to incorporate into modern wheat breeding, enhancing food security amid global challenges.
Similarly, maize (Zea mays) has undergone pangenome exploration that unveiled a range of genomic variations across different maize landraces and hybrids. This analysis revealed critical genetic factors influencing agricultural traits such as drought tolerance and nutrient use efficiency. Consequently, maize pangenome studies have potential applications in precision breeding by identifying superior genomic variants that can be utilized to create crops with enhanced resilience and productivity.
Through these case studies, it is evident that pangenome analyses offer a nuanced understanding of crop genetics, paving the way for innovative breeding strategies that can help address global agricultural challenges.
Pangenome and Agricultural Sustainability
The advent of pangenomics has opened new avenues for enhancing agricultural sustainability by providing a comprehensive understanding of plant genetic diversity. By analyzing the pangenome, which represents the entire set of genes within a species, researchers can identify specific genetic variations that confer resilience to environmental stresses. This knowledge is crucial in the context of climate change, where shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns are becoming increasingly common.
One of the key insights from pangenome studies is the ability to pinpoint genes associated with traits such as drought resistance, pest management, and nutrient utilization. For instance, certain alleles present in diverse cultivars can be selectively bred to produce crops that are better adapted to challenging conditions. This targeted approach not only contributes to higher yields but also minimizes resource input, a vital aspect of sustainable agriculture.
Moreover, the integration of pangenomic data facilitates the development of precision breeding techniques, such as CRISPR technology, which can accelerate the creation of improved crop varieties. These innovations enable farmers to cultivate crops that maintain high productivity while requiring fewer chemical inputs, aligning with the principles of organic farming and ecological stewardship.
The global challenge of food security is another area where pangenomic insights are pivotal. As the world’s population continues to grow, there is a pressing need for crops that can withstand the rigors of climate fluctuations and maintain nutritional quality. Pangenome research supports the design of multifunctional crop varieties that not only provide sustenance but also enhance soil health and biodiversity. By fostering a more resilient agricultural ecosystem, pangenomes can play an essential role in achieving long-term food security.
In conclusion, leveraging the knowledge acquired from pangenome studies stands to significantly impact agricultural sustainability. Through the promotion of robust crop varieties that thrive in diverse environmental conditions, the promise of enhanced food security and ecological balance can be realized.
Challenges in Pangenome Research
The field of pangenome research is at the forefront of plant genomics, facilitating a deeper understanding of genetic diversity and adaptability. However, it confronts several challenges that can impede its progress. One significant hurdle is the inherent genomic complexity of plants, owing to their polyploid nature and extensive structural variations. Different plant species exhibit diverse gene arrangements and copy numbers that make it challenging to establish a comprehensive reference pangenome. This complexity necessitates sophisticated genomic sequencing techniques and robust computational frameworks to map and analyze the myriad of sequences accurately.
Alongside genomic intricacies, the computational demands for processing pangenomic data are formidable. Traditional bioinformatics tools may fall short in handling the vast amounts of data generated by high-throughput sequencing technologies. This necessitates the development of advanced algorithms capable of efficiently managing large datasets and providing meaningful interpretations of the pangenomic landscape. Researchers must harness powerful computational resources, which can be both costly and time-consuming, to derive actionable insights from the data.
Data interpretation also presents significant challenges within pangenome research. Establishing the functional implications of genetic variations requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating knowledge from genomics, molecular biology, and computational sciences. Misinterpretations or oversights during this interpretative process can lead to skewed insights regarding the adaptability and evolutionary potential of plant species. Therefore, the need for interdisciplinary collaboration becomes paramount. By fostering partnerships among geneticists, biologists, and computational scientists, the scientific community can effectively address these challenges, driving forward the understanding of pangenomes and their significance in plant breeding, conservation, and climate resilience.
Future Directions in Plant Pangenome Research
The field of pangenome research in plants is evolving rapidly, and its future promises significant advancements that will reshape our understanding and application of plant genomics. One of the most compelling trends is the integration of multi-omics approaches, which combine genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. This holistic strategy allows researchers to derive a comprehensive understanding of the genetic variation within species and how this variation influences phenotypic traits such as yield, stress resistance, and adaptability. By integrating these diverse omics data, scientists can paint a clearer picture of plant biology, paving the way for innovative breeding strategies.
Precision agriculture represents another exciting frontier where pangenomics will likely play a vital role. With the increasing pressures of climate change and food security, the need for tailored agricultural practices becomes paramount. By leveraging pangenomic data, farmers could utilize genetic information to select crop varieties that are better suited for specific environments, leading to enhanced productivity while minimizing resource use. This targeted approach not only improves crop resilience to changing weather patterns but also contributes to sustainable farming practices that are critical for environmental conservation.
Furthermore, as technology progresses, the cost of genomic sequencing continues to decrease, making pangenome studies more accessible. The democratization of genomic data has the potential to foster global collaboration among researchers, facilitating a more inclusive understanding of plant diversity. It is anticipated that open-access data platforms will emerge, allowing researchers to share findings and resources, thereby accelerating discoveries in plant pangenomics.
As the field matures, attention will also be given to the ethical implications of such advancements, ensuring that innovations in plant genomics are conducted responsibly and equitably. Overall, the future of plant pangenome research holds the promise of significant contributions to agriculture and environmental sustainability, underscoring its importance in addressing global challenges.
The Role of the Research Community and Collaboration
The advancement of pangenome research in plant genomics is significantly influenced by the collaborative efforts among various stakeholders, including researchers, institutions, and industries. These collective initiatives are essential to accelerate discoveries and harness the full potential of genomic diversity in plants. Collaboration is particularly vital in pangenomics, as it integrates diverse expertise, resources, and technologies that can lead to groundbreaking developments in understanding plant genetics.
Several prominent initiatives and networks have emerged to foster collaboration in this field. The International Pangenome Consortium, for instance, plays a pivotal role in uniting researchers across numerous disciplines and geographic regions. By encouraging the sharing of data, insights, and methodologies, this consortium facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of plant adaptations and their genomic underpinnings. Additionally, various research institutions have established partnerships that promote interdisciplinary approaches to pangenome research, ultimately leading to more innovative solutions to contemporary agricultural challenges.
Industry collaboration is another critical aspect of advancing pangenome studies. Companies involved in biotechnology and agriculture are increasingly recognizing the value of genomic data in developing resilient crop varieties and enhancing food security. These partnerships between academic institutions and industries can expedite the application of pangenome findings in practical settings, thus bridging the gap between research and real-world agricultural improvements.
Furthermore, collaborative platforms such as the Plant Genomics Community of Practice offer researchers opportunities to share their findings and methodologies more broadly. Online forums and workshops are designed to ensure that knowledge is disseminated effectively, driving the momentum of pangenome research. By actively participating in such collaborative environments, the research community can tackle the challenges and complexities inherent in deciphering plant genomic diversity.
Conclusion: The Future Landscape of Plant Genomics
As we reflect on the advancements in plant genomics, it becomes evident that the exploration of the pangenome is a transformative step forward. This comprehensive genetic framework offers a more nuanced understanding of the genetic diversity present within plant species. By examining the complete set of genes, including both core and accessory genomes, researchers can decipher the complexities of plant adaptations, resistances, and overall health. This profound knowledge not only enhances our scientific understanding but also has significant implications for agricultural productivity.
The integration of pangenome research into routine plant genomics is set to revolutionize our approach to crop improvement. With a richer genetic resource, breeders can better select for desirable traits, particularly in the face of climate change and evolving pathogens. The potential for developing crops that are more resilient, nutrient-rich, and sustainable is now more attainable than ever. Furthermore, this initiative promotes biodiversity, ensuring that we do not focus solely on a limited number of cultivars but rather appreciate the full genetic spectrum available across various species.
Moreover, the implications of this research extend beyond simple crop yield increases. As our comprehension of plant genetics deepens, we can address broader challenges such as food security, nutrition, and environmental conservation. By tailoring cultivation practices to leverage the insights gained from pangenome studies, we can promote sustainable agricultural practices that are essential for future food systems.
In conclusion, the advent of the pangenome heralds a new chapter in plant genomics, intertwining research innovation with practical agricultural solutions. Bottom line, the complexities of plant genetics must be embraced and explored, as they hold the key to unlocking a sustainable future for agriculture and ensuring food security for generations to come.


